Understand the working principle! How does Ferrofluid seal maintain its sealing performance?
For those who want to understand the principle behind improving Ferrofluid seal sealing performance, this article explains:
• The types and principles of Ferrofluid seal
• The mechanism that achieves long lifespan without friction
• Examples of Ferrofluid seal applications and maintenance considerations
Learn the principles before making your choice and find the most suitable Ferrofluid seal for your needs.
Types and Principles of Ferrofluid seal
Ferrofluid seal, also known as ferrofluidic seal or ferrofluidic sealing element, is a sealing component used to prevent gas leakage in rotating machinery.
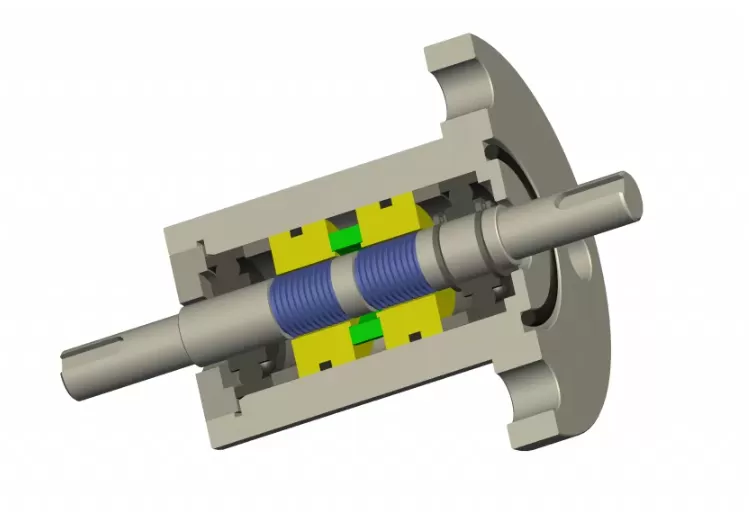
Ferrofluid Seal
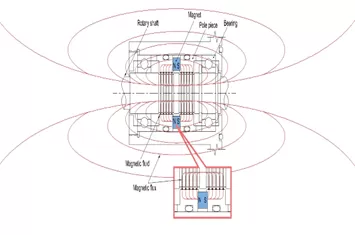
Ferrofluid seal is used for rotary sealing, preventing gas leakage through magnetic fluid and magnetic fields. Ferrofluid is a special liquid that is attracted to magnets, and by staying in the magnetic field, it achieves a sealing function.
In ferrofluid seals, magnetic liquid is fixed in the tiny gap between the rotating shaft and magnetic poles to form a seal. Traditional seals often use O-rings or oil seals, but these seals generate friction during rotation, causing wear and dust. Ferrofluid seal uses liquid magnetic fluid, and with no solid contact, it avoids friction, wear, and dust generation.
Inside the ferrofluid seal, magnets create a magnetic field between the rotating shaft and the poles. Ferrofluid stays fixed along the magnetic field lines, forming a liquid seal like an O-ring. Even when pressure differences are present, this seal effectively prevents gas leakage. The holding force of the magnetic fluid is proportional to the magnetic strength; the stronger the magnetic field, the higher the differential pressure the seal can withstand.
As a result, ferrofluid seals offer outstanding advantages, such as ultra-high vacuum, high-speed rotation, clean environments, and long lifespans compared to other sealing methods.
Choosing Between Rotating Shaft Seals and Rotary Linear Shaft Seals
Depending on the structure, Ferrofluid seal can be classified as rotary shaft seals or rotary linear shaft seals:
· Rotary Shaft Seals
These seals keep the magnetic liquid between the rotating shaft and stationary part. They are suitable for high-speed rotation, long lifespan, and clean environments. However, they are not ideal for shafts with diameters over 300mm.
· Rotary Linear Shaft Seals
These seals are used when the shaft needs to rotate and move linearly. A welded bellows is added to the flange to allow both rotational and linear motion.
Choosing between rotary shaft seals or rotary linear shaft seals depends on the application to achieve the best sealing performance.
Static Sealing vs. Dynamic Sealing
Seals can be categorized as static and dynamic. Static seals are used between fixed surfaces to prevent leakage without relative motion, while dynamic seals are used between surfaces in relative motion.
Static seals are ideal for maintaining high vacuum and low leakage rates. Dynamic seals are used in moving parts such as rotating shafts. Understanding the characteristics of each type helps in selecting the best seal to improve equipment performance and lifespan.
Achieving Long Lifespan Without Friction
Ferrofluid seal uses magnetic force to create a seal, meaning it does not generate friction as traditional oil seals or mechanical seals do. The non-friction structure is the key to the long lifespan of rotary vacuum feedthrough.
Conventional seals require periodic replacement due to friction and wear. In contrast, rotary vacuum feedthrough uses non-contact magnetic fluid to avoid these issues.
Although magnetic fluid may degrade over time, Moretec provides several types of magnetic fluid to suit different conditions. By selecting the most appropriate type, long-lasting seals can be achieved. Additionally, Moretec offers life expectancy calculations for magnetic fluid and bearings to ensure the best rotary vacuum feedthrough design.
Thus, rotary vacuum feedthrough achieves long lifespans through its non-friction structure, appropriate magnetic fluid selection, and advanced design technology.

Application Examples of Rotary vacuum feedthrough and Maintenance
Ferrofluid seal, with its excellent sealing properties, is widely used in semiconductor manufacturing equipment, vacuum devices, analytical instruments, and other industries requiring high sealing and clean environments.
Specific examples include: sputtering coating equipment, optical coatings, PVD, CVD, ion implantation devices, vacuum heat treatment furnaces, vacuum robotic arms, and crystal growth furnaces. Ferrofluid seal plays a critical role in the manufacturing process of these devices.
Ferrofluid seal’s longevity can be extended with appropriate maintenance. The main maintenance considerations are as follows:
Item | Content |
Magnetic Fluid Aging | Periodic replacement |
Checking Operating Environment | Temperature, pressure, rotational speed |
Abnormal Sound or Vibration | Early detection and handling |
Maintaining Clean Environment | Surrounding cleaning |
By adhering to these maintenance points, ferrofluid seal performance can be maintained, ensuring stable equipment operation.

Ferrofluid seal Consultation with Moretec
Ferrofluid seal, with its high technical demands and precision design, is a unique product. Moretec offers expertise in lifespan calculation, design, manufacturing, and sales, ensuring high-quality, stable products.
Clients may encounter the following issues when introducing ferrofluid seal:
Issue | Moretec Solution |
Unsure which ferrofluid seal to use | Understand the application and environment to recommend the best product |
Need a custom-shaped ferrofluid seal | Provide custom design based on extensive experience |
Need stable supply of high-quality ferrofluid seal | Quality assurance system to guarantee consistent supply |
Concerns about maintenance | Offer comprehensive after-sales support and consultation |
Moretec is committed to providing the best solutions to help customers solve their problems, with experienced staff providing detailed service.
